The new revolution which is brought by cloud computing has changed the way we store, manage, and access data completely. Moreover, a lot of businesses are looking for a platform that is inexpensive as well as which also gives productivity in hosting cloud applications.
Both platforms, OpenShift vs OpenStack, provide scalable and adaptive cloud computing solutions. However, both are suited to their specific user needs. They also differ greatly in architecture, deployment, scalability, and application support in the areas of cloud computing and container orchestration. OpenStack and OpenShift are two open-source technologies used vastly in different functionalities. OpenStack is used in managing and provisioning infrastructure resources, whereas OpenShift primarily focuses on container orchestration and application deployment.
This article will take you through a detailed review of both OpenStack and OpenShift and will also guide you in picking the best platform that fits your needs.
What is OpenStack?

OpenStack is a cloud computing platform that is free and completely open-source. It manages both public and private clouds. It is known as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) because it provides infrastructure for installing applications and operating systems.
OpenStack can manage virtual machines that run both Linux and Windows operating systems, but the control panel and many OpenStack services primarily run on Linux. OpenStack is inexpensive and it works well on commodity hardware.
These modules use APIs and various other services to manage resources like computing, storage as well as networking. It also includes a web-based dashboard for easy user interaction, as well as a stateless GUI architecture for building front-ends. The command line is the preferred mode of interface and management since it provides maximum flexibility and robustness.
When to use?
OpenStack Platform is the preferred on-site platform for managing virtual machines in a private cloud. It is used to manage storage, networking, bare-metal, and computational infrastructure, as well as virtual machines (VMs) that run on guest operating systems.
OpenStack was critical to the 3G and 4G/LTE rollouts in the telecommunications industry. Many telecommunications still rely on it to sustain those protocols’ services. Even though you have legacy apps that rely on virtualization this platform will surely offer a use case relevant to your organization.
Advantages of OpenStack:
- Cost-Effective: OpenStack is a free and open-source platform hence, the cost of creating and operating cloud infrastructure is low. Even if you utilize a managed OpenStack system, the savings are noteworthy as compared to public clouds.
- Flexibility: OpenStack is adaptable. It can be implemented in a wide range of settings. This may include public, private, and hybrid clouds.
- Scalability: OpenStack is extremely scalable because it enables you to simply add or remove as required. When you need extra resources, just add more nodes to your OpenStack Deployment. This will allow you to scale individual services separately.
- Customization: OpenStack offers a number of APIs and tools that allow businesses to modify the platform according to their needs. Therefore, this enables businesses to build a cloud architecture that matches their business needs.
- Large and active community: The community of OpenStack developers and users is large and vibrant. It provides a range of platform extensions and add-ons in addition to help and documentation.
- Security: OpenStack includes several security features such as identity and access management, encryption, and network isolation. This helps firms secure their cloud infrastructure and data.
Disadvantages of OpenStack:
OpenStack offers many benefits, but there are also probable drawbacks to consider:
- Complexity: OpenStack has so many components that make it hard for some organizations to set up and manage. It requires great investment in training and support.
- Resource requirements: OpenStack needs huge hardware resources. Thus, it is costly to deploy and maintain in comparison with choosing a hosted OpenStack solution.
- Skillset: The OpenStack product requires special skills and information for effective management. However, this may pose a challenge if an organization lacks the necessary skills.
What is Openshift?

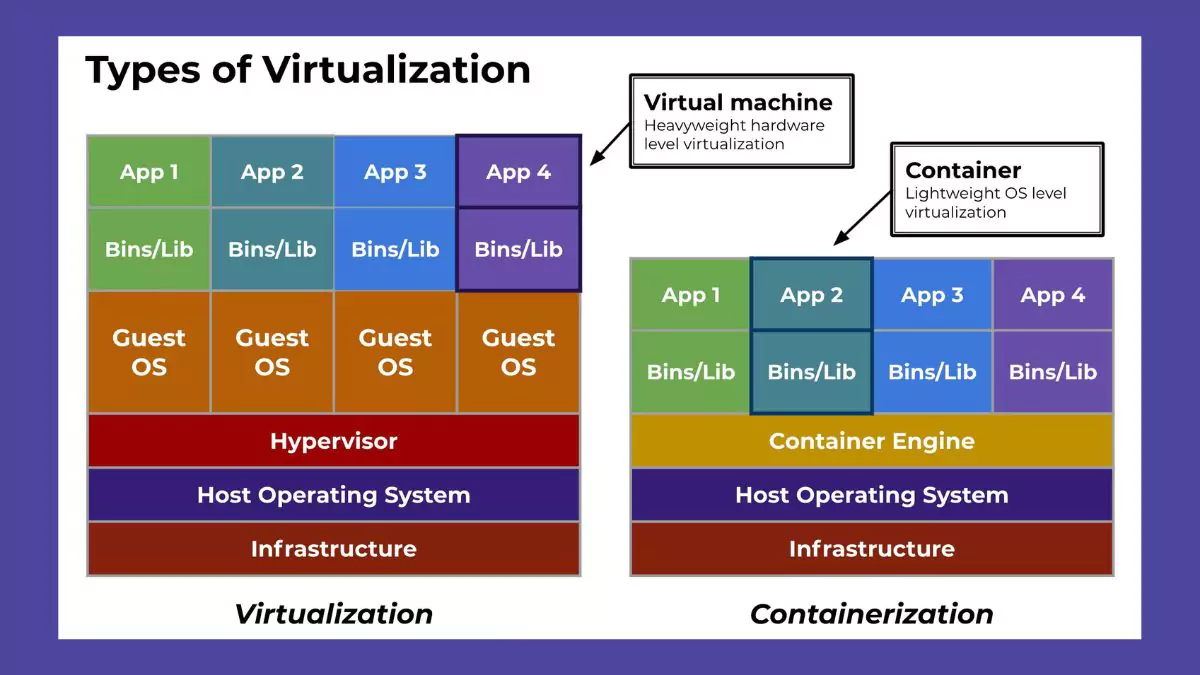
Red Hat’s OpenShift platform is a powerful software that makes it easier to install and manage container-based applications. It was constructed using Kubernetes, which is an open-source container orchestration technology.
OpenShift also allows you to manage a diverse set of apps and technologies. You can simply upgrade existing applications and speed up the delivery of new cloud-based applications. It is a versatile platform that can be used with a variety of infrastructure such as public, private, or on-site data centers.
This flexibility enables enterprises to select the infrastructure that best matches their objectives while still providing the performance, security, and compliance required.
It also includes CLI and web interface dashboards to allow developers to focus on codes, while the operations team manages and monitors the cluster. Docker containers can be deployed in OpenShift without the need to customize each Kubernetes cluster component. It’s a completely managed platform-as-a-service for container deployment.
When to use:
When businesses want to manage or update their current apps while creating new ones the cloud-native microservices usually turn to OpenShift. This flexibility provides the same user experience whether it is to deploy to the edge devices, public clouds, or on-site data centers, OpenShift makes a preferred choice.
For enterprises with many apps operating on VM-based architecture, OpenShift excels when it is used in bare metal configurations. OpenShift is available in multiple editions. It provides cloud and self-managed service alternatives.
In addition, it also offers large public cloud customers a dependable and completely built solution for their digital transformation. It is directly available from platform-as-a-service (PaaS) providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure. In short, OpenShift can help your company transition its services to containers at whichever rate makes the most sense.
Advantages of Openshift:
Ease of deployment: OpenShift indeed facilitates application deployment, but it is known to have a steep learning curve, especially for those unfamiliar with Kubernetes. The ease of deployment is relative and depends on the user’s familiarity with container orchestration tools. Therefore, this reduces the need for complex infrastructure administration. Additionally, it also allows for rapid application deployment and scaling.
- Scalability: OpenShift is scalable and it also allows companies to scale applications up or down when needed. In particular, this ensures that the applications can handle the growing traffic and demand.
- Flexibility: OpenShift can run on many different platforms.
- Programming languages and frameworks: OpenShift’s platform is flexible and thus it enables its developers to use the tools they are most comfortable with.
- Security: OpenShift offers the following features security skills, role-based access control, network isolation, and automated security updates. These features guarantee that the apps are secure.
- Community support: OpenShift is an open-source platform that is supported by a big and active community of developers. Organizations can learn the expertise of others in the community while also contributing to the platform’s development.
Disadvantages of Openshift:
Some of the weaknesses of using OpenShift include:
- Complexity: OpenShift is a complex platform that contains several components. However, this complexity is built in Kubernetes-based platforms. Therefore, a good deal of investment in training and support may be required for the full potential of the platform to be realized within an organization.
- Cost: OpenShift is a subscription or license-based program. Therefore, it is comparatively more expensive as compared to other open-source cloud application platforms.
- Vendor Lock-in: OpenShift is a Red Hat manufactured product. Therefore, it reduces the risk of vendor lock-in as compared to fully proprietary solutions.
- Limited support for programming languages: OpenShift supports a wide range of programming languages and frameworks through its support for Docker containers and Kubernetes. It is highly unlikely to encounter significant limitations in supported languages and tools.
Combining OpenStack with OpenShift for a Solid Cloud Computing Solution
While OpenStack and OpenShift share many features with each other, they are not direct rivals. Instead, they are complementary. In other words, OpenStack provides the infrastructure layer (IaaS) while OpenShift operates at the platform layer (PaaS) on top of the infrastructure. They can even collaborate to deliver a full cloud computing solution. However, OpenStack can offer the infrastructure layer on which OpenShift could run.
These two open-source solutions are intended to work together to solve different kinds of problems. Hence, when combined together they offer a very good solution for cloud computing requirements. OpenShift and OpenStack together can result in a cloud computing solution which is powerful.
Additionally, it provides excellent security features, cost savings, flexibility, scalability, and self-service. When more or less resources are added or removed, OpenShift can easily scale containerized apps.
At the same time, OpenStack can expand infrastructure resources when needed. These two can work together to give your cloud infrastructure flexibility to meet your demands.
In short, these two can make it simple for developers to provide and maintain containerized apps. It can boost output and effectiveness in the long run. IT teams can benefit from a lighter workload while handling developer requests in a short period of time. Furthermore, your apps and data are safe by OpenShift and OpenStack’s strong security capabilities.
Is Using OpenStack on OpenShift a Smart Choice for the Organizations?
If you want a strong and flexible infrastructure platform that can adapt to your organization’s changing needs, you can also consider running OpenShift on OpenStack.
Organizations using OpenShift on OpenStack can benefit from:
- Flexibility: The idea behind OpenShift is that it is well-fitted for deployment on different infrastructure platforms. OpenStack provides a highly flexible infrastructure platform to handle a wide array of workloads. When these two platforms are used together, they can actually offer a strong platform to fulfill the needs of your business.
- Cost- Effectiveness: Running OpenShift on OpenStack can save you tons of money on infrastructure costs. Since OpenStack is open-source it allows organizations to build and operate private cloud environments more cost-effectively. It is built on top of Kubernetes. OpenShift makes it possible to optimize infrastructure usage and therefore save on costs.
- Scalability: OpenShift on OpenStack allows enterprises to swiftly and effectively scale their infrastructure up or down according to their requirements. Furthermore, OpenStack enterprises may add and subtract storage and network resources as needed. On the other hand, OpenShift’s container-based architecture helps applications to scale horizontally as demand grows.
- Security: OpenStack has a high level of security and compliance such as support for multi-tenancy and network segmentation. Similarly, OpenShift assures a secure, reliable container platform that can be integrated perfectly with OpenStack security features. OpenShift on OpenStack altogether ensures that your applications can run in a safe and legal environment.
- Automation: OpenStack and OpenShift have powerful automation capabilities in their capacity to optimize IT processes. OpenShift integrates well with the automation tools of OpenStack, hence it leads to automatic application deployment, scaling, and management.
Differences Between OpenShift vs OpenStack
| OpenStack | OpenShift | |
|---|---|---|
| Objective and Use Cases | A prominent IaaS platform is used for managing virtual resources which helps businesses as well as cloud providers create flexible cloud infrastructures. | It facilitates containerized application deployment and administration with Docker and Kubernetes for developers and DevOps teams. |
| Architecture | OpenStack has a modular architecture with components such as Nova, Cinder, Neutron, and Swift which provides high control but also requires in-depth understanding. | OpenShift is based on Kubernetes, which simplifies cluster management by including components such as the Master control plane, and an Application Layer which allows developers to focus on code. |
| Ease of Deployment | Deploying OpenStack can be difficult, particularly for newbies. Tools, such as the Red Hat OpenStack Platform, can help with installation and maintenance. | OpenShift offers a simpler deployment process. Users can choose between OpenShift Container Platform (on-premises) and OpenShift Dedicated (managed service). Both of them have an installer which makes it easy to set up Kubernetes clusters and containerized apps. |
| High Availability and Scaling | OpenStack allows for horizontal growth. High availability requires careful preparation and redundancy measures, such as distributed storage, load balancing, and failover. | OpenShift, which is based on Kubernetes supports scale and high availability by design. Kubernetes capabilities such as auto-scaling and self-healing allow smooth operation amid failures. It also makes application scaling based on demand simpler. |
| CI/CD and Application Development | OpenStack doesn’t come with in-built tools for CI/CD and application development. In fact, customers have to incorporate third-party technologies in order to use them. | In comparison, OpenShift provides native application development and CI/CD support. It also provides abilities such as Source-to-Image (S2I) as well as Jenkins integration. It makes it an ideal platform for application development, testing, and deployment. |
| Community and Ecosystem | OpenStack has a big and active user community. It has several plugins and third-party integrations. It also provides a variety of commercial support alternatives. | Red Hat supports OpenShift, which provides commercial services while also maintaining a strong open-source community. Although its ecosystem is much smaller than OpenStack’s it’s ideal for enterprise use. |
| Scalability and Resource Management | OpenStack offers scalability by integrating hardware resources. It provides resource management tools such as Nova, Cinder, and Neutron, which require manual monitoring and modifications. | OpenShift takes advantage of the leading-edge resource management capabilities of Kubernetes. It automatically scales and allocates based on the CPU and memory utilization. |
| Multitenancy and Isolation | OpenStack provides multi-tenancy options for sharing infrastructure in isolation. Users set up virtual networks, assign resources, and use RBAC policies for security. | OpenShift amplifies the multi-tenancy capability of Kubernetes. Though the Kubernetes namespaces serve to provide basic isolation, OpenShift is enhanced with security features such as network restrictions, RBAC, and project-based quotas. This assures secure maintenance of teams or projects in one cluster. |
| Management and Deployment of Applications | While OpenStack easily deploys infrastructure resources, it does not have a natively deployed facility for application deployment and administration. Users take advantage of other tools to fill this gap, which results in deployment taking longer with more complex workflows. | OpenShift excels at app deployment and management with technologies such as Source-to-Image. Kubernetes with Helm charts facilitates application deployment, scalability, and management. Also, CI/CD pipelines built with Jenkins or Tekton automate the application lifecycle which increases developer efficiency. |
| Ecosystem and Integration | OpenStack offers a large ecosystem that allows customers to design cloud environments while it also needs attention to handle its diversity and integrations. | OpenShift is compatible with Kubernetes which eases the connection with Kubernetes tools and services. Such as users are allowed to extend and enhance the benefits of containerized applications using Helm charts, and Kubernetes-native monitoring/logging solutions. |
| Commercial Support | OpenStack manufacturers like Red Hat, Canonical, as well as Mirantis, provide commercial support and distributions, which improve deployment and management with new capabilities. | It is sponsored by Red Hat which offers commercial support including services such as on-site solutions to ensure corporate stability and robustness. |
Also, know the difference between OpenShift vs Docker vs Kubernetes
Conclusion
To conclude, OpenShift vs OpenStack offer separate functions in cloud computing and container orchestration. OpenStack is an IaaS that actually supports infrastructure management and virtualization, while OpenShift is a PaaS for container orchestration and application development.
Moreover, OpenStack can be more suitable in cases when a more flexible infrastructure platform for the private or public cloud creation is needed.
On the other hand, if you want to deploy applications in a containerized manner and want to do it fast, then OpenShift offers much ease and friendliness for developers.